Laying intermediate rafter insulation - instructions and costs

- The intermediate rafter insulation
- The attachment
- Possible problems
- Meaning of the material
- The properties of different materials
- Rock wool / glass wool
- Styrofoam
- hemp
- wood fiber
- sheep wool
- cellulose
- The cost of the insulation
- The combination with a sub-rafter insulation
Saving energy is an important issue today. Rising heating costs put a heavy burden on the household budget, so modernization reduces expenditure. The insulation can be applied both to a new building, an expansion as well as a modernization. However, they not only benefit from the savings, but also from the increase in living comfort, the rising value of the building and the relief of the environment. Therefore, find out how best to apply when installing an inter-rafter insulation.
Bad or missing roof insulation leads to a high loss of heating heat. On average, this results in a heat loss of about 30 percent through the roof. The effectiveness of the insulation depends on the material selected, the quality of the installation and the form of construction. A distinction is made between different approaches, such as rafter insulation, under rafter insulation and intermediate rafter insulation. The latter variant is considered the classical method and is mainly used for pitched roofs. It can also be used in attics used as living space and ensures a high level of living comfort.
The intermediate rafter insulation
In this variant of the insulation, the gaps between the rafters are isolated. The advantages are the relatively low cost and the ease of installation. You cut the insulating material precisely to us and insert it according to our instructions.
Advantages:
- Insulating mats can be easily installed
- Insulating effect higher than with a sub-rafter insulation
- Inter-spar renders are cheaper than rafter insulation
Disadvantage:
- existing panels must be removed
- theoretically, the formation of thermal bridges is possible
- Mounting the vapor barrier is relatively cumbersome
The attachment
Step 1:
First, you may need to remove existing old insulation and cladding. You now have to be able to see the roof truss and the bricks.
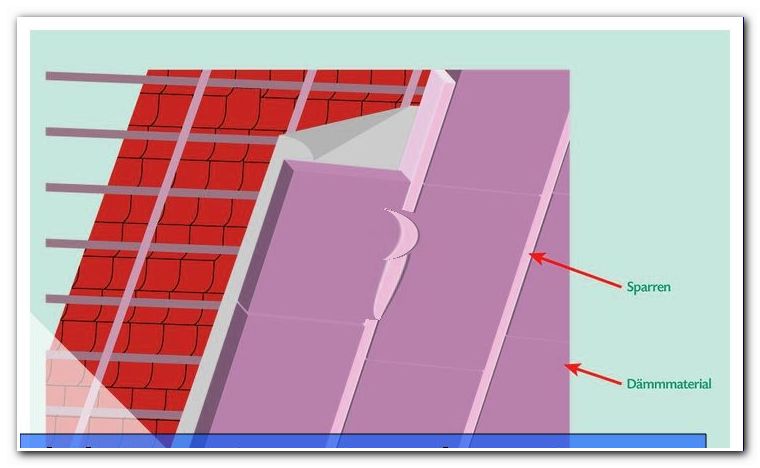
Step 2:
Trim the chosen insulation material.
Step 3:
Now clamp the insulating material in the spaces between the rafters.
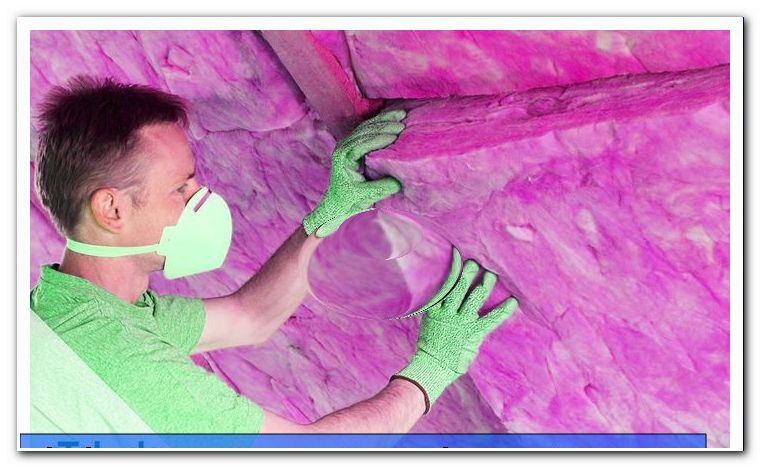

Step 4:
Attach a vapor barrier. This prevents moisture from entering the insulation in the room and causing damage here.
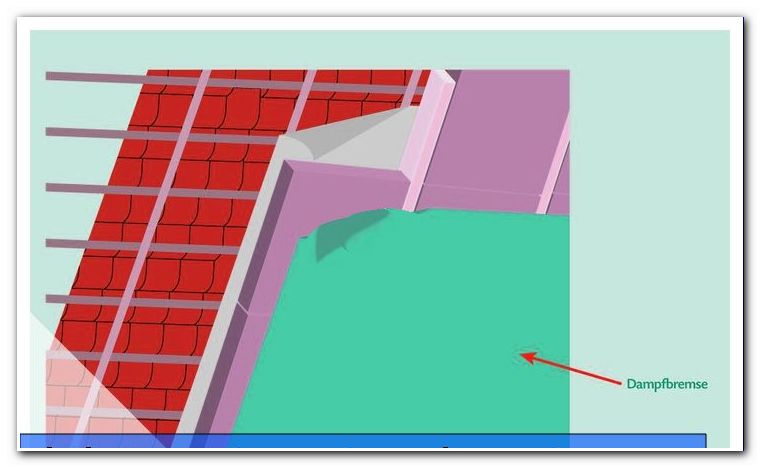
Possible problems
- The rafters are not high enough.
In this case, you can not attach sufficient insulation material. Therefore, screw on additional squared timbers from below. This procedure is also called doubling.
- It comes to mold growth
Mold can form when moisture penetrates the insulation. Therefore, attach a vapor barrier. It is mounted below the insulation, in the direction of the attic.
Meaning of the material
The material is crucial to the effectiveness of the insulation and must therefore be chosen carefully. In addition to quality but also the price plays a crucial role.
What is the thermal conductivity coefficient ">
- Rock wool / glass wool
- Styrofoam
- hemp
- wood fiber
- sheep wool
- cellulose
The properties of different materials
Rock wool / glass wool
Rock wool is one of the classics in roof insulation and is characterized by its low price. At the same time, the material has good insulation properties.

Advantages:
- Rock wool has a reflective coating that prevents cooling or heating.
- is easy to work with.
- is resistant to mold.
- Building material is difficult to ignite.
- Insulating material is relatively inexpensive.
Disadvantage:
- For the production of a high energy consumption is necessary. Therefore, rock wool is not one of the sustainable and environmentally friendly materials.
- The subsequent disposal costs consequential costs, because rock wool is not compostable.
- During laying, mouth and mucous membranes are irritated.
- Contact with moisture can lead to loss of insulation properties.
Glass wool basically has the same properties as rock wool.
The fibers of rock wool / glass wool cause itching, redness and swelling on the skin. Therefore, you should wear suitable protective clothing when laying and cutting. In any case, gloves and long-sleeved clothing are necessary. With a disposable suit you protect your own clothes.
Tip: If you have accidentally come into contact with the rock wool / glass wool, wash the skin off with cold water . If you were to use warm water, then the fibers could settle in the skin.
Styrofoam
Styrofoam is a synthetic-organic insulating material derived from petroleum. The basis for the production forms a plastic, which is deformed by means of heat. It is a commonly used insulation material because it is inexpensive to buy and effective in effect. It is offered in the form of plates and is therefore easy to install.

Advantages:
- good insulation properties
- no rotting
- inexpensive
- versatile, suitable for different types of insulation
Disadvantage:
- in a fire, toxins are released
- In production, a high energy consumption is necessary
- made from non-renewable raw materials
- If the material shrinks then joints are created
- Mold formation possible, as diffusion-proof
hemp
Hemp is made of natural fibers and is harmless to health. It is a sustainable building material, which therefore serves as an alternative to environmentally hazardous materials.
Advantages:
- has only a slight tendency to rotting
- is durable and durable
- is resistant to pests and resistant
- is a sustainable material
- the addition of boron salt ensures fire protection
- Hemp is offered in slabs, mats and in loose form
- suitable for allergy sufferers
- Hemp is compostable, which reduces later disposal costs.
- is moisture-balancing, which prevents the formation of mold and dust.
Disadvantage:
- The fire protection is given, however, is classified only as "normal".
- Insulation must be thicker because the insulating effect is even greater with other materials.
wood fiber
The insulation wood fiber is made of spruce, pine and fir. It is shredded wood, which is mixed with water. The resulting wood pulp is processed into plates. These are used in both the intermediate spar insulation and the rafter insulation and are characterized by their naturalness.

Advantages:
- Wood fiber is free of chemical additives
- Wood fiber is relatively environmentally friendly.
- the building material is compostable.
- Fabric is uncomplicated when laying and can be processed well.
- is vapor-permeable, reducing the risk of mildew.
Disadvantage:
- Processing may cause respiratory irritation and skin irritation.
- Wood fiber is assigned to fire protection class B2 (normally inflammable).
sheep wool
Sheep's wool is an ecologically beneficial insulation. The main area of application is in the field of intermediate rafter insulation.
Advantages:
- Sheep wool has good heat and sound insulation.
- The building material is characterized by the natural moisture absorption. This means that around one third of its own weight can be absorbed without losing its insulating properties.
- Sheep's wool has a pollutant-reducing effect. It is capable of breaking down formaldehyde.
- The insulating material can be processed relatively easily.
Disadvantage:
- normally flammable
- Sheep wool mats are not particularly pressure-resistant.
- Sheep wool is not resistant to rotting and insects.
cellulose
Cellulose is a natural substance that can be produced, for example, from single-grade papers. Various additions produce good fire protection. The special feature of this building material is that it is harmless to health and suitable for allergy sufferers. The advantages, however, are often offset by a higher price.
The peculiarities of cellulose
It is an organic insulating material that is harmless to health. Another advantage is the resistance to mold and vermin. Even the soundproofing can convince.
Apply cellulose afterwards
In general, cellulose is used as blow-in insulation. Here, the building material is blown into cavities in the form of loose bulk insulation. As a result, the thickness can be set and varied precisely and the costs decrease compared to variants in sheet form. Cellulose can be compacted and pressed very well resulting in a tight fit. The biggest advantage comes from the environmental friendliness. The material is made from recycled waste paper and is free from toxic chemicals. The production itself requires a low energy consumption. Due to the nature and the starting materials later disposal is easy and leads to low follow-up costs.
Tip: When blowing in, fine dust is formed so that you must wear suitable protective clothing, especially a breathing mask.
Cellulose can also be bought in the form of plates. However, these will easily crumble when carelessly cutting, so you need a little practice.
The cost of the insulation
The insulation between the rafters is relatively inexpensive and at the same time effective. Another advantage is that the attachment is quick. In contrast to insulation on the rafters, no new covering of the roof is necessary. The costs thus depend primarily on the material used. On average, you have to expect expenses of 50 to 80 euros per square meter, if you hire a specialist. By contrast, if you carry out the work yourself, then you can already purchase Klemmfilz for less than 5 euros per square meter. However, it is important to pay attention to a clean way of working. Errors later have a negative impact on the energy balance of the house. Also, the bonding of the vapor barrier film must be done wisely, otherwise moisture enters the insulation. Below you will find an overview of the average material costs of the respective building materials: 
- Rock wool / glass wool: 10 to 20 euros per m²
- Styrofoam: 5 to 20 euros per m²
- Hemp: 10 to 27 euros per m²
- Wood fiber: 40 to 50 euros per m²
- Sheep's wool: 15 to 25 euros per m²
- Cellulose: 10 to 20 euros per m²
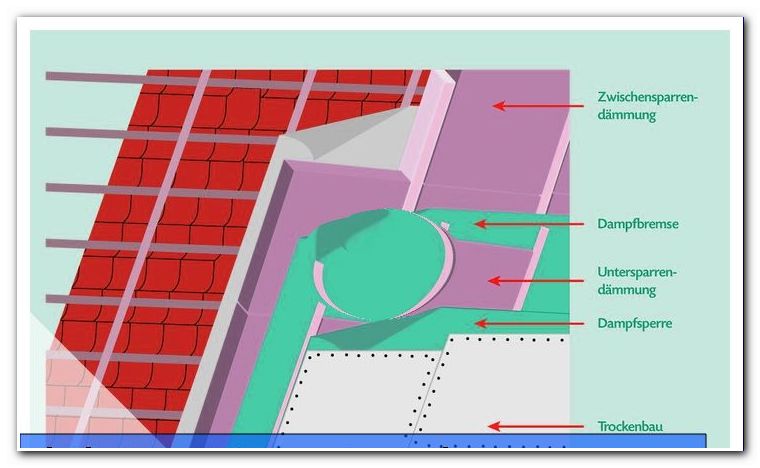
There are funding opportunities available "> The combination with a Untersparrendämmung
If you install the insulation later, then you must consider what effect you want to achieve. In general, it is advantageous to additionally install a sub-rafter insulation. First of all lay the intermediate rafter insulation and subsequently apply the under rafter insulation. For this purpose, strips are screwed onto the roof battens, which are at 90 degrees to the lathing. Subsequently, the filling with the selected insulation material.
Tips for quick readers:
- Inter-rafter insulation with:
- sheep wool
- hemp
- Rock wool / glass wool
- Styrofoam
- wood fibers
- cellulose
- can be combined with under rafter insulation
- Cut construction material
- Apply vapor barrier film
- Apply for a grant from KfW-Bank
- Note the properties of the individual materials
- Cellulose is considered to be particularly environmentally friendly
- pay attention to the fire protection




