Table: Energy consumption value - what is good, what is bad?

- Demand card & consumer badge
- Does energy consumption value
- Proper application
- Read the characteristic values
- Lower heating costs
- Positive values
Since 1 May 2014, an energy certificate must be presented for every property sold or rented. From this document, the annual cost of heating energy can be calculated. A buyer or tenant of a house or apartment is better protected against nasty surprises. However, interpreting and converting the information from the energy certificate is not easy.
Demand card & consumer badge
First of all, you have to differentiate between the "demand badge" and the "consumer badge". The demand card is an indication of how much energy is needed to heat a house via theoretically determined data. The amount of theoretically necessary heating energy is measured by:
- Construction of the house
- Isolation of the facade
- Tightness and insulation effect of the windows
- Type and condition of the heating system
- Insulation from the roof
- General condition of the house
- Isolation of the radiator pipes
Basically, it is quite true that the more invested in the professional insulation and high-quality heating technology, the heating costs should be reduced proportionally. But this is, as I said, only a theoretical value.

In order to obtain a practically comprehensible proof of whether the theoretically determined data actually led to the desired saving effect, the consumption certificate was introduced. This indicates how much heating energy has been consumed in the last three years. That is a comprehensible, empirical value. However, he has an unknown: not everyone keeps to the recommended value of 21 ° C. Therefore, the information from the consumption certificate always depends on the heating behavior of the previous owner or previous tenant.
Does energy consumption value
What exactly does the energy consumption parameter indicate?>
- How much energy
- For heating
- of one square meter
to the recommended 21 ° C was needed. Its unit of measure is kilowatt hour per year times area or kWh / (a × m²).
Proper application
... of the energy consumption characteristic value
To determine the heating costs as accurately as possible, proceed as follows:
1. Multiply the characteristic value by the square meters of the residential unit
If you multiply the characteristic value with the square meters of the housing unit, two things happen:
- It creates a comprehensible value for the entire house
- The unit of square meters is shortening
Example:
If you have a residential unit with an area of 120 m² and an energy consumption value of 200 kWh / (a × m²), you will get the indication of 24000 kWh / a.
2nd surcharge of 20%
The energy consumption value is again multiplied by 1.2. It takes into account the staircases, basements and other little-used rooms, which also belong to the residential unit.
In a pure electric heating, which is certainly the most expensive form of heating of all, you get so theoretically on annual heating costs of about 6000 + 20% = 7200 €. Here you can see how important an efficient heating with a cheap heat source is. For comparison: When heating with gas prices start at about 5 cents per kWh.
Read the characteristic values
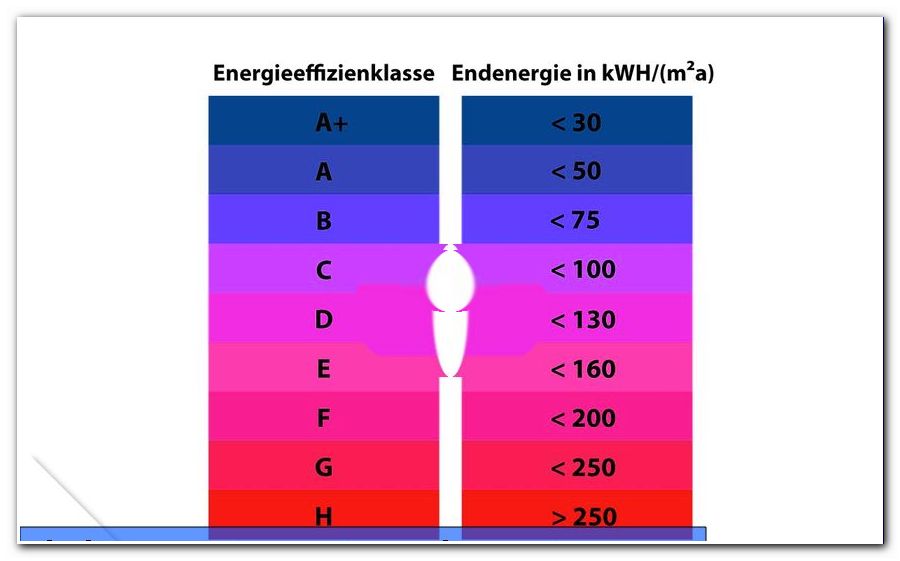
The characteristic values are indicated on a scale, which is also highlighted in color. This allows a prospective buyer to recognize at a glance what he claims to be buying or renting a home. The following table is intended to break down the usual information for consumers:
- Over 400 - red: Not energetically renovated house, very high costs for heating
- 310 - 400 - orange: Slightly energetically renovated house
- 260 - 310 - yellow: Average renovated building
- 210 - 250 - greenish-yellow: Acceptable to well-renovated building
- 150 - 200 - green: Detached house, built to modern standards
- 60 - 140 - green: multi-family house, built to modern standards
- 0-50 - green: passive house
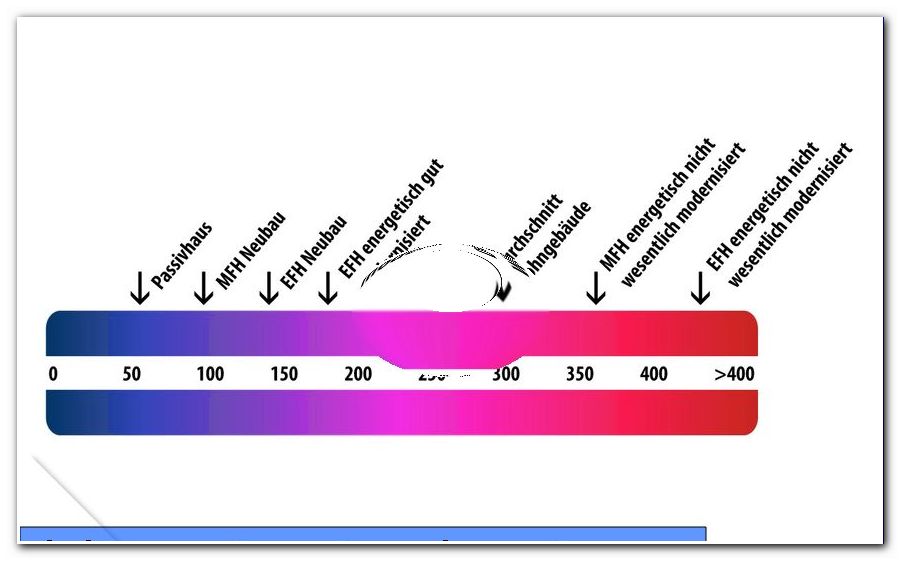
A value of "0" in the table is actually theoretically achievable. However, the necessary investments are very high. The buildings known as Passive Houses are indeed capable of producing more energy than they consume. But for this the following technical measures are necessary:
- Multi-layer external insulation
- Use of photovoltaic and solar thermal
- Ideal orientation to the sun
- cogeneration
- Heat pumps with storage
- energy storage
All these measures can easily double the purchase price of a home. Conversely, you should be alerted if a value of over 300 or more is in the table. Such a poorly renovated house is today hardly meaningfully habitable. Bad insulation not only means high heating costs. Also, such houses are usually quite wet and prone to mold.
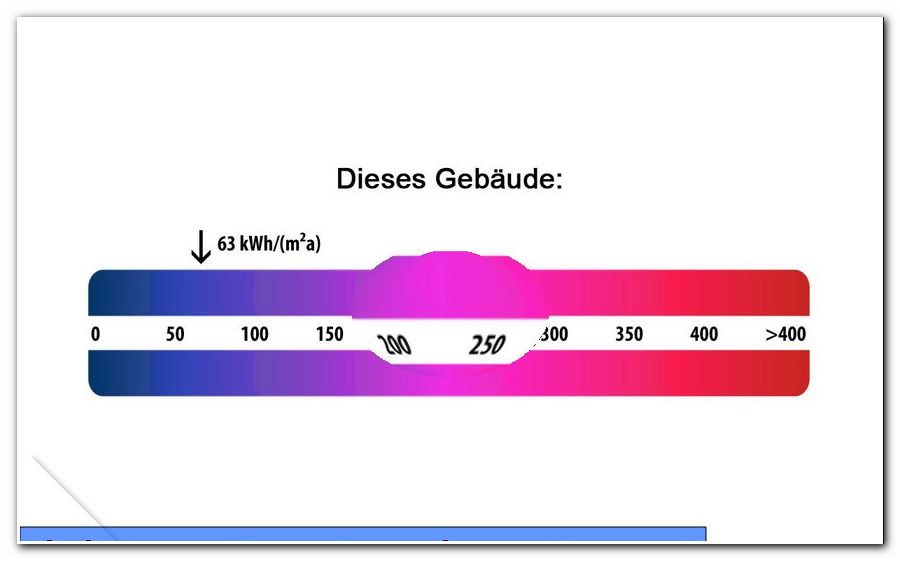
Lower heating costs
However, surprisingly inexpensive measures can already do a lot to reduce energy consumption in your home. The simplest and cheapest measure is to insulate the pipes from the radiator. Anyone can do this themselves in home work and thus lowers their heating costs by at least 10%. Another 10% can be achieved if the radiators are carefully vented. This is very easy and has an immediate, positive effect.
Hydraulic balancing can also be done by yourself. This increases the efficiency of your heating system. Each room is thus heated equally well, no matter how far away from the central heating.
Positive values
If the energy consumption parameter from the table shines in the rich green, it should still be inquired. The styrofoam massively installed in recent years has now proven to be a real problem. Not least the fire disaster in London has alarmed the western world. Styrofoam is indeed a cheaper, and easy to process insulation material. But even if he ensures a good value in the table - dispose of it is now a nightmare.
The cost of disposing of old Styrofoam has grown astronomically. As a tenant of a styrofoam insulated apartment remains a queasy feeling. However, a buyer of a house with excellent energy-to-energy rating should ask exactly how this good value was achieved in the table. If the insulation costs have been kept low by sticking generously polystyrene, you buy yourself a time bomb. Although a facade insulated with polystyrene ensures a good value in the table of the energy consumption value, it must be replaced after 15 to 20 years. The costs of dismantling and, above all, disposal then cancel out all the savings in the area of heating costs.
We therefore recommend using more environmentally friendly and non-critical insulation materials. Recommended are:
- rock wool
- glass wool
- expanded clay
- calcium silicate
- excelsior
- impregnated sheep wool
- paper granules
- foam glass
If you want to renovate your house energetically, then you rely on these uncritical insulation materials. They cost a little more in the acquisition. For this they increase the value of their house considerably. Potential buyers are increasingly deterred by polystyrene. Therefore, now should be set to higher quality and sustainable alternatives.




